Cybersecurity is a growing concern for organisations across the globe. To help show the growing risk of cybercrime and how it impacts business, in this article we’ve compiled some of the key UK and US cybercrime statistics for 2022.
Cybercriminals are taking advantage of the trends that impact workforces worldwide. This includes the shift to remote working, use of cloud services, the side effects of the global pandemic, and importantly increasing their own collaboration on online criminal forums. This is driving an upward trend in the number of attacks, the cost of attacks, and the wider repercussions they cause.
Because of the increased risk and prevalence of cyber-attacks, in October 2021, Lindy Cameron the chief executive of the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre warned that “Ransomware presents the most immediate danger to the UK businesses and most other organisations.”
Cyber-attacks can be extremely disruptive to organisations, with critical business systems often being offline from a few days to weeks or months. It is important to make sure cybersecurity is a board-level concern and ensure there is a dedicated budget and resources are aligned.
Number of ransomware attacks in the UK in 2021
According to the UK’s Information Commissioners Office (ICO), there were 654 reported ransomware attacks in the UK in 2021. This is more than double the 326 that were reported in 2020.
Source: https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/report/weekly-threat-report-1st-april-2022
Number of ransomware attacks in the US in 2021
According to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), there were 3,729 reported ransomware attacks in the US in 2021. This is an increase of over 33% compared to the 2,474 incidents reported in 2020.
Source: https://www.cisa.gov/uscert/ncas/alerts/aa21-243a

The average duration of downtime after a ransomware attack from 1st quarter 2020 to 4th quarter 2021
The average downtime a company experiences after a ransomware attack is 22 days.
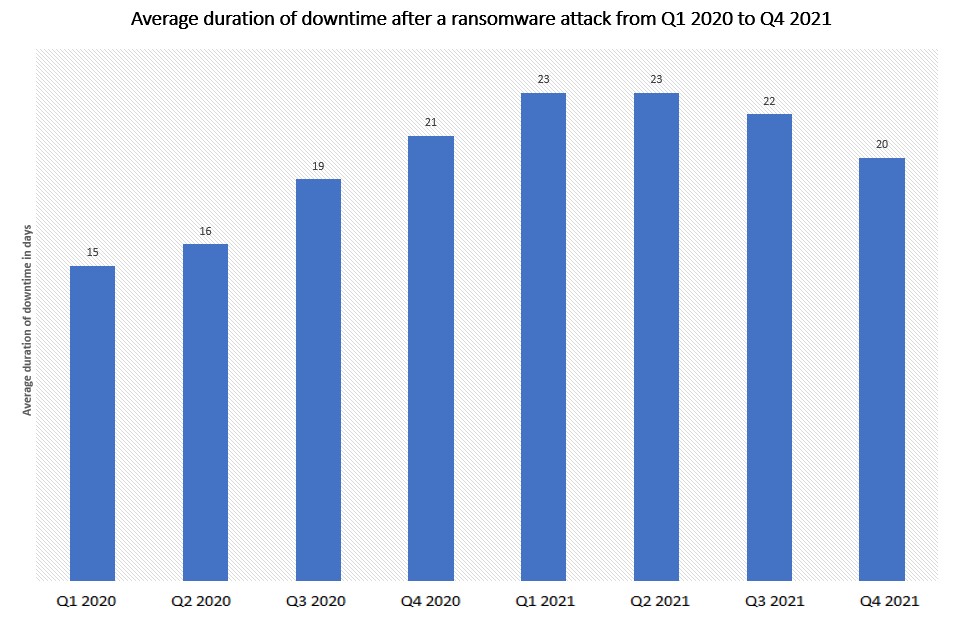
Source: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1275029/length-of-downtime-after-ransomware-attack/
Total number of incidents handled by the UK NCSC in 2021 was 777
Source: https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/
Other UK and US cybercrime statistics:
The US was the target of 46% of cyberattacks in 2020, more than double any other country
14 of the 16 US critical infrastructure sectors were targeted with ransomware in 2021
Source: https://docs.house.gov/meetings/JU/JU00/20220329/114533/HHRG-117-JU00-Wstate-VorndranB-20220329.pdf
Ransomware complaints in the US increased by 82%, with a 449% rise in ransom payments between 2019 to 2021
The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) reports that this is only a fraction of the incidents out there, which makes trends difficult to track with certainty.
Source: https://docs.house.gov/meetings/JU/JU00/20220329/114533/HHRG-117-JU00-Wstate-VorndranB-20220329.pdf
As of March 2022, the FBI is investigating more than 100 ransomware variants which have been used in multiple ransomware campaigns
Source: https://docs.house.gov/meetings/JU/JU00/20220329/114533/HHRG-117-JU00-Wstate-VorndranB-20220329.pdf
US citizens lost more than $6.9 billion to internet crimes in 2021
This is a jump of more than $2 billion from 2020, according to the FBI’s annual Internet Crime Report. The report, contains “information about the most prevalent internet scams” reported to the federal law enforcement agency’s Internet Crime Complaint Center.
A total of 847,376 internet crime complaints were filed in 2021, a 7% increase from 2020 but a staggering 81% jump from 2019, according to the FBI.
96% of organization were targeted by an email-related phishing attempt
While phishing is the most common email-borne threat, data leaks and business email compromise attacks are not far behind.
Source: https://www.mimecast.com/state-of-email-security/
27.7% of online traffic is bad bots
Imperva Threat Research team estimates that 27.7% of online traffic is bad bots. These bad bots are now more advanced and evasive than ever, mimicking human behaviour in ways that make them harder to detect and prevent. They allow bot operators, attackers, unsavoury competitors, and fraudsters to perform a wide array of malicious activities. Web scraping, competitive data mining, personal and financial data harvesting, scalping, account takeover fraud, spam and transaction fraud are just a few of these activities.
Source: https://www.imperva.com/resources/resource-library/reports/bad-bot-report/
Biggest distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack recorded was a 3.47 Tbps attack
Microsoft’s Azure DDoS Protection team said that in November 2021, it fended off what industry experts say is likely the biggest distributed denial-of-service attack ever: a torrent of junk data with a throughput of 3.47 terabits per second.
Microsoft mitigated a 3.47 Tbps attack, which originated from approximately 10,000 sources and from multiple countries across the globe, including the United States, China, South Korea, Russia, Thailand, India, Vietnam, Iran, Indonesia, and Taiwan.
Source: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/azure-ddos-protection-2021-q3-and-q4-ddos-attack-trends
By 2023, the total number of DDoS attacks worldwide will be 15.4 million
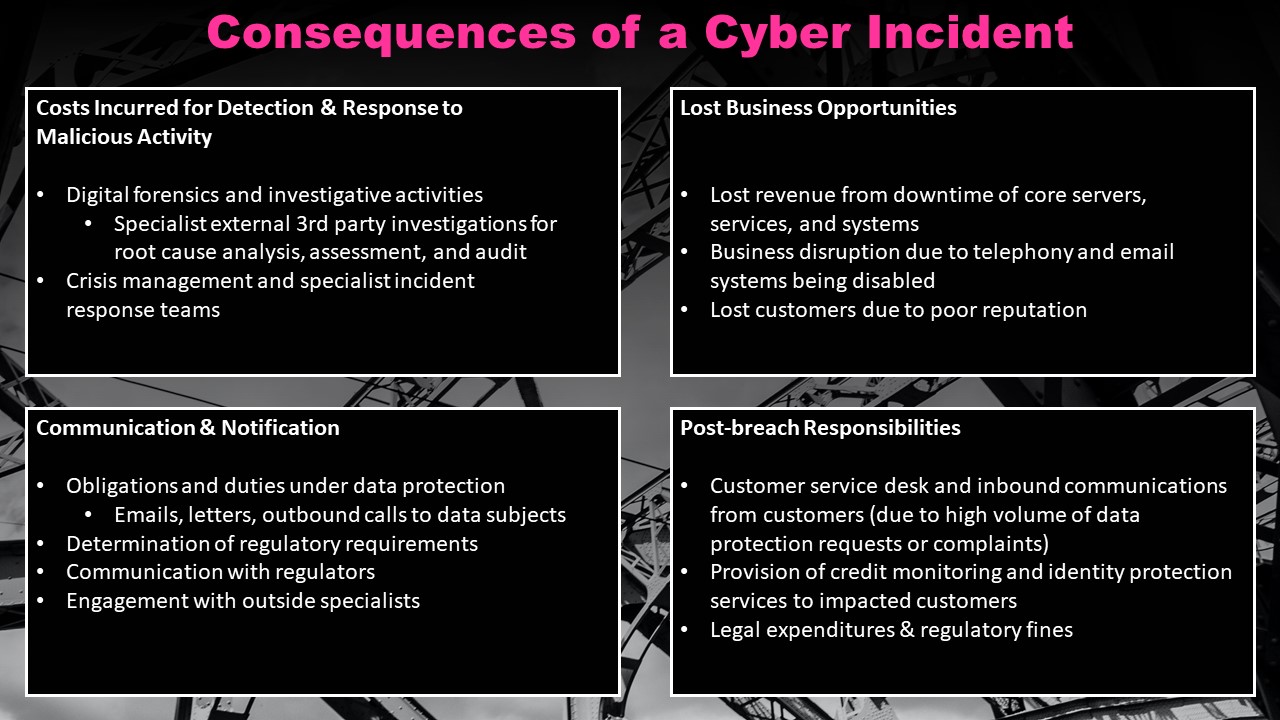
Examples of a Cyber Incident (Defined by the UK National Cyber Security Centre):
- Malicious code: Malware infection on the network, including ransomware
- Denial of Service: Typically a flood of traffic taking down a website, can apply to phone lines, other web facing systems, and in some cases internal systems.
- Phishing: Emails attempting to convince someone to trust a link/attachment.
- Unauthorised Access: Access to systems, accounts, data by an unauthorised person (internal or external) – for example access to someone’s emails or account.
- Insider: Malicious or accidental action by an employee causing a security incident.
- Data breach: Lost/stolen devices or hard copy documents, unauthorised access or extraction of data from the network (usually linked with some of the above).
- Targeted attack: An attack specifically targeted at the business – usually by a sophisticated attacker (often encompassing several of the above categories).
Next Steps
It is advisable to review the websites of the UK National Cyber Security Centre and the US Critical Infrastructure Security Agency. Both organisations, regularly post best practice and guidelines for protecting against ransomware attacks. You can view these pages here:
https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/guidance/mitigating-malware-and-ransomware-attacks
https://www.cisa.gov/uscert/ncas/alerts/aa20-245a
How We Can Help
If you have a cybersecurity incident, believe you are under attack or have been compromised, then call us immediately for assistance on 020 7193 4905 or email us as incident [at] first-response.co.uk
Managed cybersecurity services can help prevent ransomware attacks by detecting and stopping attacks at the initial stage of the attack cycle, our managed detection & response includes an extended detection & response platform with full 24/7 coverage by our security operation centre (SOC), our managed cybersecurity services are detailed here.
Not every attack can be prevented, therefore it is important to have a plan in place should the worst happen. Details on our cyber incident response plans and readiness is available here.
